
in this digital world demands speed, agility, and intelligence from enterprise systems. Traditional ERP systems often fail to meet these expectations due to their complexity and performance bottlenecks. This is where SAP S4HANA Architecture shines. Designed to harness the power of in-memory computing and modern interfaces, S4HANA delivers real-time insights, streamlined processes, and simplified operations.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unpack everything about SAP S4HANA Architecture: from its history and core design principles to deployment options, benefits, and future innovations.
What is SAP S4HANA?
SAP S4HANA (SAP Business Suite 4 SAP HANA) is the next-generation ERP suite built exclusively for the SAP HANA in-memory database. Unlike earlier ERP systems that relied on traditional databases, S4HANA combines transaction processing and analytics in a single platform. This allows organizations to analyze vast amounts of data in real-time while executing complex business processes seamlessly.
Why SAP S4HANA Matters in Modern Enterprises
Businesses today need more than just data storage; they need insight-driven decision-making. With globalization, supply chain complexities, and digital commerce trends, the demand for real-time intelligence has skyrocketed. SAP S4HANA empowers enterprises to:
- Reduce IT landscape complexity
- Simplify workflows
- Enable predictive analytics
- Deliver personalized user experiences
By adopting SAP S4HANA, organizations future-proof their operations while staying competitive in the digital economy.
Evolution of SAP ERP to S4HANA
From R/2 to R/3: The Legacy Systems

SAP began with R/2 in the 1970s, operating on mainframes. The evolution to SAP R/3 introduced a client-server architecture in the 1990s, revolutionizing ERP by providing a modular design and relational database integration.
SAP ECC and Its Limitations
SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) was built on the AnyDB approach, meaning it could run on multiple databases like Oracle, IBM DB2, or Microsoft SQL Server. While versatile, ECC suffered from data redundancy, batch-driven processes, and slower performance.
The Switch to SAP S4HANA
To address these issues, SAP launched S4HANA in 2015, designed exclusively for HANA in-memory computing. This move eliminated traditional database dependencies and introduced a simplified data model, real-time analytics, and Fiori-based user experience.
Core Principles of SAP S4HANA Architecture
In-Memory Computing with SAP HANA Database
The backbone of S4HANA is the SAP HANA database, which stores data in-memory (RAM) instead of disks. This ensures lightning-fast data retrieval and enables advanced analytics like predictive modeling, machine learning, and simulations.
Simplified Data Model
Traditional ERPs often relied on multiple tables, indexes, and aggregates. SAP S4HANA removes redundancies by introducing a single line-item table concept, which reduces data footprint and improves efficiency.
Real-Time Analytics and Transaction Processing
Unlike legacy systems that separated OLAP (analytics) and OLTP (transactions), SAP S4HANA unifies both in one system, enabling simultaneous processing without performance compromises.
Key Components of SAP S4HANA Architecture
SAP S4HANA is built on a layered architecture that ensures flexibility, scalability, and performance. To truly understand its power, we need to explore its three key layers:
SAP HANA Database Layer
At the foundation lies the SAP HANA database, which is in-memory and columnar by design. Unlike conventional databases that store information on disk, SAP HANA processes everything in main memory (RAM). This architecture eliminates latency and supports real-time data analysis.
Key features include:
- Columnar storage: Optimizes both read and write operations.
- Compression techniques: Reduce storage requirements by up to 80%.
- Parallel processing: Allows simultaneous execution of queries, boosting speed.
The result is a platform that can handle transactions and analytics in one system, a massive shift from the traditional ERP model.
Application Layer
Above the database lies the application layer, which houses the business logic. This is where enterprise processes—such as finance, logistics, human resources, and procurement—are executed.
With S4HANA, this layer is designed to be leaner and more efficient than in previous ERP systems. Redundant tables and aggregates have been eliminated, and the simplified data model makes reporting and analytics much easier.
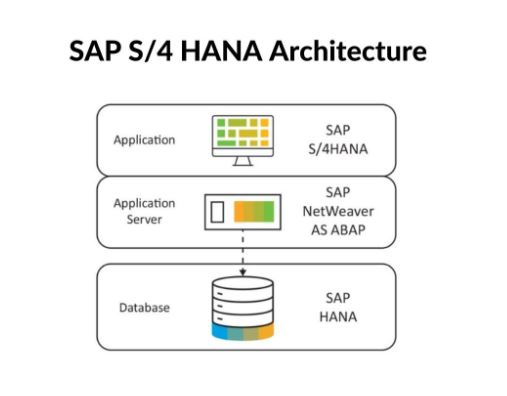
Presentation Layer (SAP Fiori)
The presentation layer represents the user interface. SAP Fiori, the default UX for S4HANA, replaces the older SAP GUI with a modern, role-based design.
Key benefits of SAP Fiori include:
- Responsive design: Works on desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Role-based dashboards: Employees see only the information they need.
- Intuitive navigation: Reduces training time and enhances productivity.
Together, these three layers create a seamless architecture that bridges the gap between complex enterprise data and user-friendly applications.
Deployment Options of SAP S4HANA
One of the strengths of SAP S4HANA Architecture is its deployment flexibility. Companies can choose the model that best suits their strategy, IT landscape, and budget.
On-Premise Deployment
The on-premise model means the system is installed and managed in the company’s own data centers.
Advantages:
- Full control over infrastructure and security.
- Ability to customize deeply according to business needs.
- Suitable for industries with strict compliance requirements.
Disadvantages:
- Higher upfront investment in hardware and maintenance.
- Longer deployment timelines.
Cloud Deployment
The cloud version of S4HANA, managed by SAP or hyperscalers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), is increasingly popular.
Advantages:
- Faster implementation and scalability.
- Lower upfront costs, with subscription-based pricing.
- Automatic updates from SAP, ensuring constant innovation.
Disadvantages:
- Less customization compared to on-premise.
- Dependency on internet connectivity.
Hybrid Model
The hybrid deployment combines the strengths of on-premise and cloud. For example, sensitive financial data can remain on-premise, while less critical operations run on the cloud.
This model is ideal for companies in transition phases or those seeking both control and flexibility.
Integration Capabilities in SAP S4HANA
In today’s interconnected digital world, no ERP system can exist in isolation. SAP S4HANA is designed with strong integration capabilities, enabling smooth connectivity with both SAP and non-SAP systems.
SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP)
The SAP BTP acts as the backbone for extensions, integrations, and innovations. It offers:
- Analytics services for deep insights.
- Integration Suite to connect applications across landscapes.
- AI and ML services to enhance decision-making.
APIs and Extensions
S4HANA comes with a wide set of standard APIs. These APIs allow developers to integrate third-party applications, build custom extensions, and automate workflows.
For example, integrating an e-commerce platform with S4HANA ensures that order data flows automatically into the ERP system, streamlining order fulfillment.
Integration with Third-Party Systems
Enterprises often rely on multiple systems, such as Salesforce, Oracle, or custom apps. SAP S4HANA supports:
- Middleware integration (SAP PI/PO, SAP CPI).
- Direct API integration for real-time data exchange.
- Data services for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes.
This flexibility ensures S4HANA fits seamlessly into diverse IT environments.
Security and Compliance in SAP S4HANA Architecture
With data breaches and cyber threats on the rise, security is at the heart of SAP S4HANA Architecture.
Data Encryption and Privacy
SAP HANA provides end-to-end encryption at multiple levels:
- Data-at-rest encryption ensures stored data is secure.
- Data-in-transit encryption secures communication between layers.
- User data privacy features support GDPR compliance.
Role-Based Access Control
S4HANA adopts a role-based security model, ensuring that employees only access the information relevant to their roles. This reduces risks of unauthorized access while improving efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance Support
SAP provides built-in compliance features to help companies adhere to regulations like:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act)
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
By embedding compliance into the architecture, SAP ensures that businesses can operate confidently across multiple geographies.
Benefits of SAP S4HANA Architecture

Organizations investing in SAP S4HANA reap a wide range of benefits.
Performance and Speed
Thanks to in-memory computing, tasks that once took hours—like financial closing—can now be completed in minutes. Businesses can run complex simulations and forecasts almost instantly.
User Experience with SAP Fiori
SAP Fiori transforms user experience with intuitive interfaces and personalized dashboards. Employees can access workflows, reports, and KPIs from any device, improving productivity and engagement.
Lower Total Cost of Ownership
While the initial investment may seem high, S4HANA reduces overall IT costs by:
- Eliminating redundant systems.
- Simplifying infrastructure.
- Reducing data storage needs.
- Automating updates in the cloud model.
This combination often results in long-term savings
FAQs
Q1. What is SAP S4HANA architecture in simple terms?
It’s a modern ERP system structure built on an in-memory database that integrates transactions, analytics, and AI into one platform.
Q2. How is SAP S4HANA different from ECC architecture?
Unlike ECC, which relied on disk-based databases and complex data models, S4HANA uses in-memory computing and simplified structure
Q3. What role does SAP Fiori play in S4HANA architecture?
SAP Fiori provides the modern, intuitive interface for users, offering real-time insights and mobile accessibility.
Q4. Can businesses customize SAP S4HANA architecture?
Yes, companies can extend it via in-app customization, BTP side-by-side extensions, and ABAP coding.
Q5. Is SAP S4HANA more secure than traditional ERP?
Yes. It offers role-based access, data encryption, and compliance-ready features.
Q6. What industries benefit most from S4HANA architecture?
Industries like manufacturing, finance, retail, and healthcare benefit from its real-time analytics and AI-driven automation.
Conclusion: The Future of SAP S4HANA Architecture
SAP S4HANA architecture represents a paradigm shift in how enterprises manage operations. By combining in-memory technology, simplified data models, AI, and cloud capabilities, it empowers organizations to make real-time decisions, scale faster, and stay competitive.
The future of ERP is intelligent, adaptive, and cloud-first—and SAP S4HANA’s architecture is paving the way for this transformation
